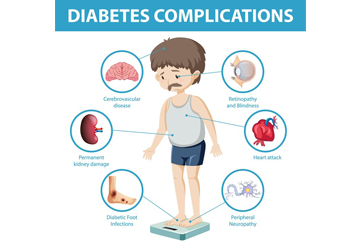
Diabetes can be caused by a combination of genetic factors, lifestyle choices, and environmental influences. Type 1 is primarily genetic and autoimmune, while Type 2 is often linked to obesity and lifestyle.
- 83 8008 0059
- 1st Floor, Chavan Mohite Complex, Umbrya Ganpati Chowk Dhayari, Pune